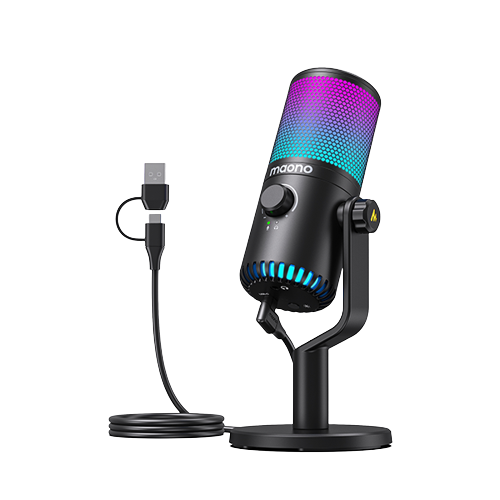
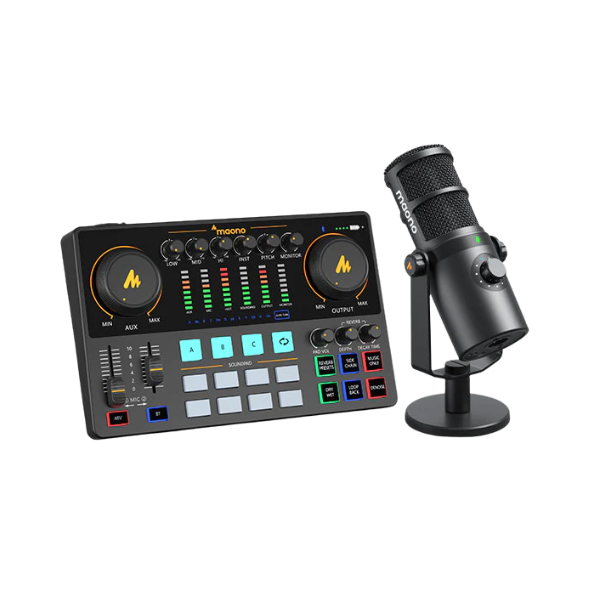
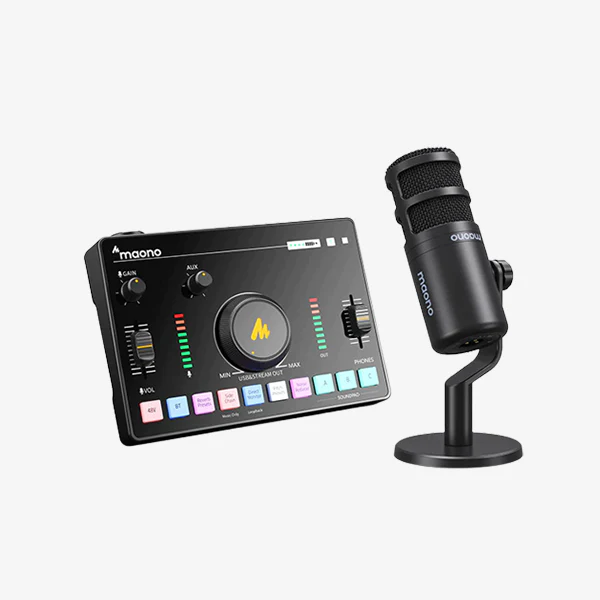
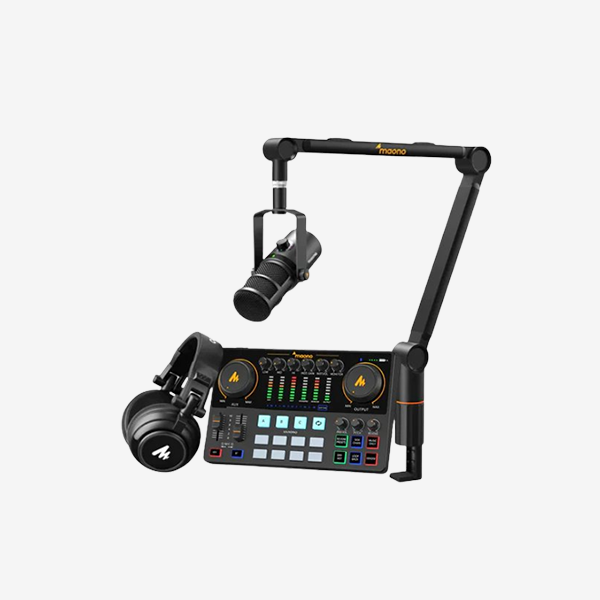
Audio signals can be compressed based on audio compression technology. Audio
compression technology refers to the use of appropriate digital signal processing techniques
for the original digital audio signal stream (PCM encoding) to reduce (compress) its code rate
without loss of useful information or negligible loss.
It is called compression coding. It must have a corresponding inverse transform called
decompression or decoding. Audio signals may introduce a large amount of noise and
certain distortion after passing through a codec system.
In the field
of audio compression
there are
two compression methods
lossy compression
and lossless compression. Commonly known MP3, WMA, and OGG are called lossy
compression.
As the name implies, lossy compression reduces the audio sampling frequency and bit rate,
and the output audio file will be smaller than the original file. Another type of audio
compression is called lossless compression, which is the subject matter to be said.
Lossless compression can compress the volume of the audio file less than 100% of all the
data of the original file, and restore the compressed audio file to achieve the same size and
the same code rate as the source file.
The lossless compression formats are APE, FLAC, WavPack, LPAC, WMALossless,
AppleLossless, La, OpTImFROG, Shorten, and the common, mainstream lossless
compression formats are APE and FLAC.